Calculate your paving materials and costs in seconds. Get accurate quantities for blocks, slabs, stones, and installation estimates for any project size.
Paving Calculator
Your ultimate tool for precise paving project planning
Project Details
Enter the details for your paving project to get comprehensive calculations.
Area Calculation
Material Details
Sub-base Requirements
Cost Estimation Details
Area Results
Visual Representation
Enter dimensions to see visual representation
Total Area
Perimeter
Materials Required
Enter project details to calculate materials
Cost Breakdown
Calculate materials first to see cost estimates
Professional Installation Guide
Step-by-step guide following best practices and industry standards
Planning & Preparation
- Check for underground utilities before excavation
- Obtain necessary permits for front garden paving
- Consider drainage requirements (Building Regulations)
- Mark out the area with spray paint or pegs
Excavation
- Excavate to required depth (typically 200-250mm total)
- Create proper falls for drainage (1:40 minimum)
- Compact the formation level
- Install edge restraints if required
Sub-base Installation
- Lay MOT Type 1 aggregate in 75mm lifts
- Compact each lift with a vibrating plate
- Check levels and falls regularly
- Install geotextile membrane if specified
Bedding Layer
- Prepare 5:1 sharp sand and cement mortar
- Lay bedding layer 40-50mm thick
- Screed to correct levels and falls
- Work in manageable sections
Paving Installation
- Start from a straight edge or corner
- Lay slabs with consistent joint widths (8-15mm)
- Check levels with a spirit level regularly
- Cut slabs with appropriate tools
Pointing & Finishing
- Point joints with appropriate mortar
- Clean excess mortar from slab surfaces
- Allow 24-48 hours before light traffic
- Apply sealant if required
Industry Compliance & Standards
BS 7533-101:2021
Structural design of pavements using modular paving units
BS 7533-102
Installation of pavements surfaced with modular paving
Building Regulations
Drainage requirements for paved areas over 5m²
Planning Permission
Required for non-permeable front garden paving over 5m²
Planning a paving project requires precise calculations to determine material quantities and costs. A paving calculator eliminates guesswork, providing accurate estimates for your outdoor surface projects. Whether you’re installing a new driveway, patio, or garden path, understanding how these calculators work saves time and money.
Our Other Construction Tools:
- Cement Ballast Calculator UK – 2025
- Self Leveling Concrete Calculator UK
- Sand Calculator: How Much Sand Do I Need?
What is a Paving Calculator?
A paving calculator is a digital tool that computes the exact amount of paving materials needed for your project. It calculates square footage, material quantities, and estimated costs based on your specific measurements and chosen materials. These calculators factor in essential variables like waste allowance, material type, and installation depth.
Modern paving calculators handle various materials including block paving, natural stone, concrete slabs, and resin surfaces. They provide instant results, eliminating manual calculations and reducing material ordering errors. Professional contractors and DIY enthusiasts rely on these tools for accurate project planning.
How Much Paving Do You Need?
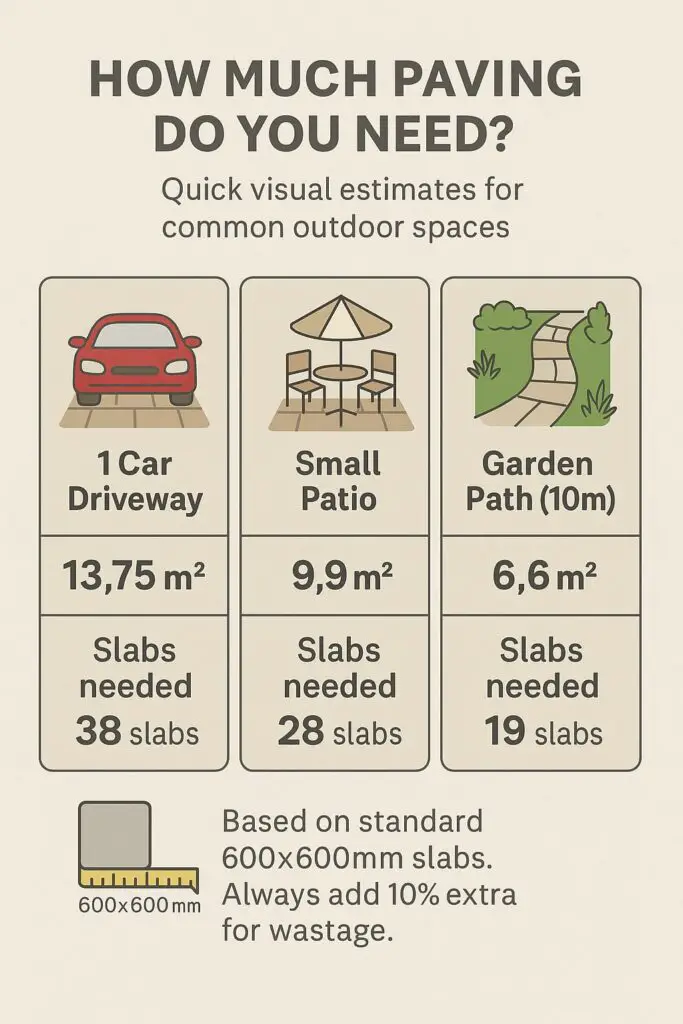
How Does a Paving Calculator Work?
Input Requirements
Paving calculators require specific measurements to generate accurate results. You’ll need the length and width of your paving area in metres or feet. For irregular shapes, break the area into rectangular sections for easier calculation.
The calculator also needs material specifications including paver size, thickness, and type. Some advanced calculators request additional details like mortar joint width and sub-base requirements. Weather conditions and site accessibility may influence certain calculations.
Calculation Methods
The calculator multiplies length by width to determine total area coverage. It then calculates material quantities based on individual paver dimensions and adds a waste factor typically ranging from 5-10%. Labour costs are estimated using regional pricing data when available.
Complex calculations include sub-base material requirements, edge restraints, and jointing compounds. The system automatically adjusts for different paving patterns that may require additional materials or cutting waste.
Types of Paving Materials and Their Costs
Block Paving
Block paving remains popular for driveways and patios due to its durability and aesthetic appeal. Standard concrete blocks cost £15-25 per square metre, whilst premium clay pavers range from £30-50 per square metre. Installation typically adds £20-35 per square metre to total project costs.
Block paving calculators account for different laying patterns including herringbone, stretcher bond, and basketweave. Each pattern affects material requirements and cutting waste differently.
Natural Stone Paving
Natural stone offers premium aesthetics with materials like sandstone, limestone, and granite. Prices vary significantly from £25-80 per square metre depending on stone type and quality. Indian sandstone provides cost-effective options around £20-35 per square metre.
Stone paving calculations must consider irregular sizes and thickness variations. Premium stones often require specialist cutting tools and experienced installers, increasing overall project costs.
Concrete Paving
Concrete slabs provide affordable paving solutions ranging from £10-25 per square metre. Modern concrete offers various textures, colours, and finishes mimicking natural materials. Installation costs are generally lower due to larger slab sizes reducing labour time.
Concrete paving calculators factor in standard slab dimensions and recommend appropriate sub-base depths for different applications.
Resin Bound Paving
Resin bound surfaces offer permeable paving solutions increasingly popular for environmental compliance. Material costs range from £40-80 per square metre with professional installation required. These surfaces provide excellent drainage and smooth accessibility.
Resin calculators determine aggregate quantities, resin ratios, and preparation requirements for proper installation.
Essential Measurements for Paving Calculations
Area Calculation Methods
Accurate measurements form the foundation of reliable paving calculations. Use a measuring tape to record length and width dimensions, noting any obstacles or irregular boundaries. For curved areas, use the string method to outline shapes before measuring.
Break complex areas into simple geometric shapes: rectangles, triangles, and circles. Calculate each section separately, then combine totals for overall area requirements. Digital measuring tools and smartphone apps can improve measurement accuracy.
Depth Requirements
Paving depth depends on intended use and traffic loads. Pedestrian areas typically require 50-75mm paving thickness, whilst vehicle access needs 80-100mm depth. Heavy traffic areas may require reinforced specifications up to 150mm.
Standard Depth Guidelines
| Application | Paving Depth | Sub-base Depth |
|---|---|---|
| Garden Paths | 50mm | 75mm |
| Patios | 60mm | 100mm |
| Domestic Driveways | 80mm | 150mm |
| Commercial Areas | 100mm | 200mm |
Sub-base depth requirements vary based on soil conditions and expected loading. Clay soils typically need deeper sub-bases compared to well-draining sandy conditions.
Paving Calculator Formula and Manual Calculations
Basic Area Formula
The fundamental paving calculation uses the simple formula: Area = Length × Width. For rectangular areas, multiply these dimensions to get square meterage. Triangle areas use Area = ½ × Base × Height, whilst circles require Area = π × Radius².
Complex shapes benefit from grid overlay methods or breaking into manageable sections. Smartphone apps can calculate irregular areas using GPS coordinates or photo analysis.
Material Quantity Calculations
Once you’ve determined total area, calculate material requirements using individual paver dimensions. Standard block pavers (200mm × 100mm) provide 50 units per square metre. Natural stone varies significantly, requiring specific supplier calculations.
Add 5-10% waste allowance for straight laying patterns and 10-15% for complex designs requiring extensive cutting. Professional installations may require less waste due to experienced cutting techniques.
Wastage Factor Considerations
Different paving patterns create varying waste levels:
| Pattern Type | Waste Factor |
|---|---|
| Stretcher Bond | 5-7% |
| Herringbone | 8-10% |
| Random Pattern | 10-15% |
| Complex Curves | 15-20% |
Factor additional materials for edge cutting, breakages during installation, and future repairs.

Factors Affecting Paving Costs in 2025
Material Prices
Paving material costs fluctuate based on supply chain factors, fuel prices, and demand patterns. Natural stone prices increased approximately 15-20% during 2024 due to transportation costs and quarry limitations. Concrete products remain relatively stable with minor inflationary adjustments.
Imported materials face additional cost pressures from currency exchange rates and shipping delays. Local materials often provide better value and faster delivery times.
Labour Costs
Installation labour represents 40-60% of total paving project costs. Skilled paving contractors charge £150-250 per day depending on experience and location. Complex installations requiring specialist techniques command premium rates.
Urban areas typically have higher labour costs compared to rural locations. Seasonal demand affects pricing, with spring and summer commanding peak rates.
Additional Expenses
Beyond materials and labour, consider additional costs including site preparation, waste removal, and equipment hire. Excavation may require mechanical diggers costing £200-300 per day. Skip hire for waste removal adds £150-300 depending on size requirements.
Planning permission or building regulations approval may apply to certain projects, adding administrative costs and time delays.
Step-by-Step Guide: Using a Paving Calculator
Begin by measuring your paving area accurately using a measuring tape. Record all dimensions including length, width, and any irregular features. Sketch the area noting obstacles like manholes, trees, or existing structures.
Select your preferred paving material from the calculator database. Input material specifications including size, thickness, and laying pattern. Some calculators request sub-base requirements and edge restraint details.
Enter your measurements into the calculator interface. Review calculations checking for obvious errors before proceeding.
The calculator generates material quantities, estimated costs, and installation requirements. Print or save results for supplier quotations and contractor discussions. Compare multiple material options to optimise budget allocation.
Visit suppliers like Marshalls or Bradstone to verify pricing and availability using calculator results.
Common Paving Calculator Mistakes to Avoid
Measurement Errors
Inaccurate measurements represent the most common calculator error source. Double-check all dimensions using multiple measurement methods. Failing to account for slopes, steps, or level changes affects material requirements significantly.
Record measurements clearly noting which dimension represents length versus width. Confusion between these values creates calculation errors requiring material reordering and project delays.
Material Waste Miscalculations
Underestimating waste requirements creates material shortages during installation. Different laying patterns require varying waste allowances often underestimated by inexperienced users. Complex curves and intricate designs always need additional cutting allowance.
Overestimating waste increases project costs unnecessarily. Balance conservative planning with cost efficiency using historical data from similar projects when available.
Paving Cost Breakdown and Budget Planning
Material Costs Table
| Material Type | Cost per m² | Installation per m² | Total per m² |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete Blocks | £15-25 | £20-30 | £35-55 |
| Clay Pavers | £30-50 | £25-35 | £55-85 |
| Natural Stone | £25-80 | £30-45 | £55-125 |
| Resin Bound | £40-80 | £20-30 | £60-110 |
Prices include standard installation techniques and may vary based on complexity and location. Specialist applications or difficult access increase costs significantly.
Labour Cost Estimates
Professional installation ensures quality results and warranty coverage. Labour costs vary by region and contractor experience. Obtain multiple quotations comparing scope, timeline, and warranty terms.
DIY installation reduces costs but requires tool investment, time commitment, and skill development. Consider hiring professionals for complex preparations whilst completing final laying personally.
Specialist Paving Applications
Driveway Paving
Driveway paving requires enhanced structural specifications to support vehicle loading. Use minimum 80mm paving thickness with 150mm compacted sub-base. Consider drainage requirements and connection to existing road surfaces.
Block paving driveways offer excellent durability and easy maintenance. Permeable options help manage surface water runoff complying with sustainable drainage requirements.
Patio Paving
Patio installations focus on aesthetic appeal and comfort underfoot. Natural stone provides premium appearances whilst concrete offers cost-effective solutions. Consider drainage falls directing water away from buildings.
Larger format materials reduce joint lines creating cleaner appearances. Heating elements can be incorporated for year-round outdoor use extending seasonal enjoyment.
Garden Path Calculations
Garden paths require careful width planning ensuring comfortable pedestrian access. Standard 1.2-1.5 metre widths accommodate single-file walking whilst 1.8+ metres allow passing. Consider wheelchair accessibility requirements where applicable.
Curved paths need flexible materials or careful cutting techniques. Calculate additional waste for radius cutting and consider contrasting borders highlighting path edges.
Professional vs DIY Paving Installation
Professional installation guarantees quality workmanship with warranty protection. Contractors possess specialist tools, experience, and supplier relationships ensuring efficient project completion. They handle planning permissions, utilities identification, and disposal requirements.
DIY installation offers significant cost savings but requires substantial time investment and skill development. Consider tool purchase or hire costs, physical demands, and potential quality compromises. Simple rectangular areas suit DIY approaches whilst complex designs benefit from professional expertise.
Research local building regulations ensuring compliance with drainage, accessibility, and structural requirements. Some installations may require professional certification or inspection.
Conclusion
Paving calculators provide essential tools for accurate project planning and cost estimation. Understanding their operation and limitations ensures successful material ordering and budget management. Whether pursuing professional installation or DIY approaches, these calculators eliminate guesswork and reduce costly errors.
Modern digital tools offer sophisticated features including 3D visualisation, real-time pricing, and mobile accessibility. However, basic calculation knowledge remains valuable for verification and custom applications. Combine calculator results with professional advice for complex projects ensuring optimal outcomes.
Successful paving projects begin with accurate calculations. Invest time in proper measurement and material selection using reliable calculator tools. This foundation supports quality installations providing years of functional and aesthetic satisfaction.
Frequently Asked Questions
How accurate are online paving calculators?
Online paving calculators provide accuracy within 5-10% when supplied with correct measurements and specifications. Digital tools excel at standard applications but may require manual adjustments for unique circumstances. Always verify results with supplier recommendations and professional consultation for large projects.
What’s the standard wastage allowance for paving?
Standard wastage allowances range from 5-15% depending on laying pattern complexity and installer experience. Simple stretcher bond patterns need 5-7% waste whilst complex herringbone or curved designs require 10-15%. Professional installers typically need less waste than DIY projects due to cutting expertise.
How do I calculate paving for irregular shapes?
Break irregular shapes into simple geometric sections including rectangles, triangles, and circles. Calculate each section separately using appropriate formulas, then combine totals. Digital measuring apps can calculate irregular areas using GPS coordinates or photo analysis for complex shapes.
What factors increase paving installation costs?
Several factors increase installation costs including difficult site access, extensive excavation requirements, complex drainage needs, and intricate laying patterns. Sloping sites, existing surface removal, and utility relocations add significant expenses. Premium materials and specialist finishes also command higher prices.
Can I use a paving calculator for different materials?
Most paving calculators accommodate various material types including blocks, slabs, and loose materials. Select appropriate material specifications within the calculator ensuring accurate sizing and coverage calculations. Different materials may require adjusted waste factors and installation techniques affecting final quantities and costs.
