Calculate grout quantities instantly with our free online tool. Enter your tile size, joint width, and area to get precise material estimates. Accounts for waste factors and different grout types – no maths needed, just accurate results.
Professional Grout Calculator
Calculate exact grout quantities for your tiling project
Project Details
Room Dimensions
Tile Specifications
Grout Specifications
Our Other Tools:
- Cement Ballast Calculator UK – 2025
- Self Leveling Screed Calculator
- Concrete Calculator UK: Free Ready-Mix Estimator for Builders
- Sand Calculator: How Much Sand Do I Need?
Planning a tiling project requires precise calculations, and determining the right amount of grout is crucial for both budget and project success. A grout calculator eliminates guesswork, ensuring you purchase the correct quantity whilst avoiding costly mistakes and project delays.
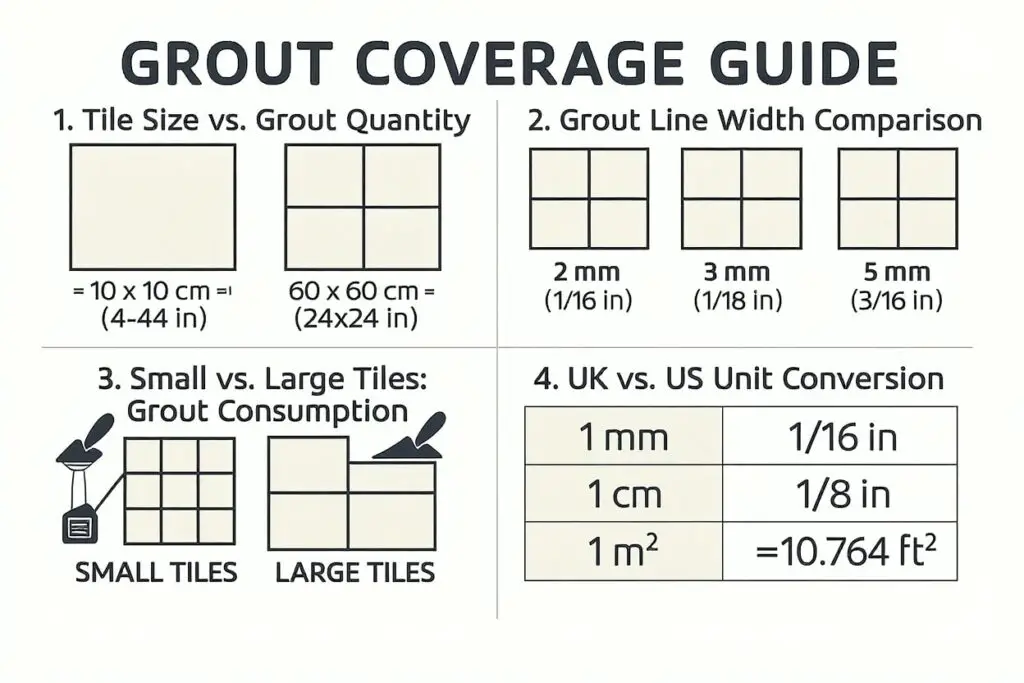
What is a Grout Calculator?
A grout calculator is a mathematical tool that determines the exact amount of grout needed for your tiling project based on specific parameters. These calculators consider tile dimensions, joint width, joint depth, and surface area to provide accurate material estimates.
Modern grout calculators use advanced algorithms that account for waste factors, grout type variations, and application methods. They transform complex mathematical formulas into user-friendly interfaces, making professional-level calculations accessible to DIY enthusiasts and contractors alike.
Why Use a Grout Calculator?
Accurate grout estimation prevents material shortages that can halt your project mid-installation. Purchasing insufficient grout often results in colour variations between batches, compromising your finished appearance.
Conversely, overestimating leads to unnecessary expenses and storage issues. Professional contractors report that proper grout calculation reduces material costs by 15-20% whilst improving project timelines significantly.
Grout calculators also help determine mixing requirements, ensuring consistent application throughout your project. This consistency directly impacts the durability and aesthetic quality of your finished installation.
Types of Grout and Their Coverage
Cement-Based Grout
Cement-based grout remains the most common choice for residential projects due to its affordability and versatility. This grout type typically covers 25-30 square feet per 25-pound bag, depending on joint dimensions and tile specifications.
Standard cement grout requires careful water ratios, typically 1:4 to 1:5 water-to-powder ratio. Coverage varies significantly based on joint width, with narrow joints requiring less material per square foot than wider applications.
Epoxy Grout
Epoxy grout offers superior stain resistance and durability but requires different calculation methods due to its unique composition. A single epoxy grout kit typically covers 35-50 square feet, depending on joint specifications and tile porosity.
This grout type costs significantly more than cement-based alternatives but provides excellent longevity in high-traffic areas. Professional installation often justifies the additional expense through improved performance characteristics.
Urethane Grout
Urethane grout combines durability with flexibility, making it ideal for areas with temperature variations. Coverage rates typically range from 40-60 square feet per container, depending on manufacturer specifications and application conditions.
This grout type requires minimal mixing and offers excellent workability, reducing installation time while maintaining professional results.
How to Calculate Grout Quantity Manually
Basic Formula for Grout Calculation
The fundamental grout calculation formula considers tile dimensions, joint specifications, and surface area:
Grout Volume = (Length + Width) × Tile Thickness × Joint Width × Number of Tiles
This formula provides the basic volume calculation, which must then be adjusted for specific grout types and waste factors.
Step-by-Step Manual Calculation Process
Begin by measuring your total installation area in square feet. Multiply length by width to establish the base coverage area requiring grouting.
Next, determine your tile specifications including length, width, and thickness. These measurements directly impact grout requirements and must be accurate for proper calculation.
Calculate joint dimensions by measuring the intended gap between tiles and the depth of penetration required. Joint depth typically equals 75% of tile thickness for optimal structural integrity.
Apply the coverage formula using your specific measurements, then add 10-15% waste factor to account for mixing losses and application variables.
Factors Affecting Grout Coverage
Tile Size and Thickness
Larger tiles require proportionally less grout per square foot due to fewer joint intersections. A 12×12 inch tile installation uses approximately 40% less grout than a 6×6 inch tile installation covering the same area.
Tile thickness directly correlates with grout volume requirements. Thicker tiles create deeper joints, significantly increasing material needs. Natural stone tiles often require additional grout due to irregular thickness variations.
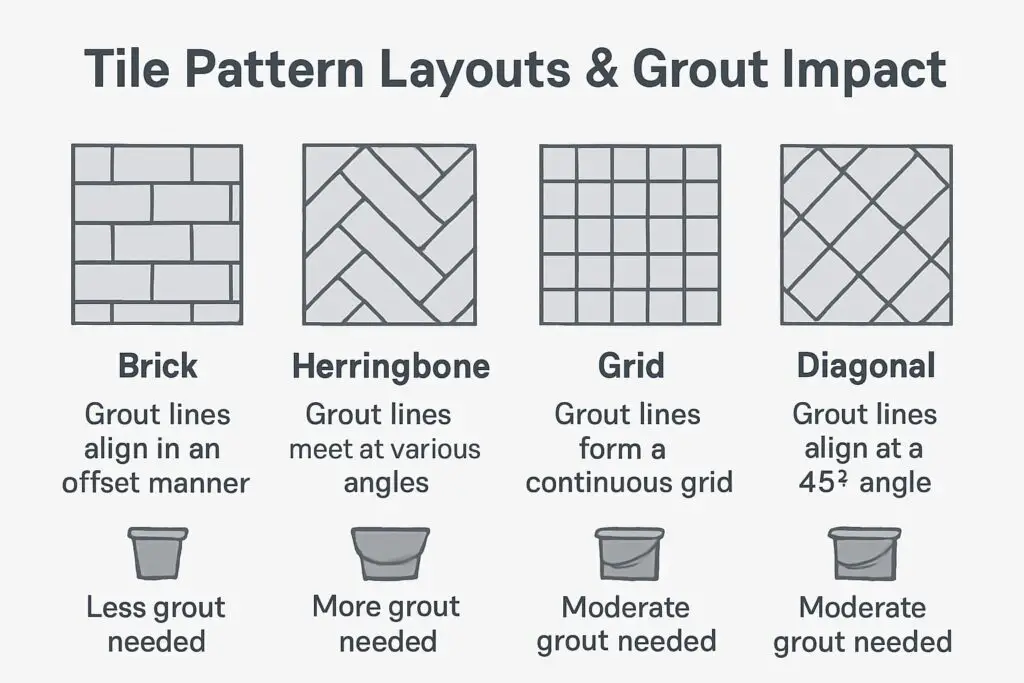
Joint Width and Depth
Joint width dramatically impacts grout consumption, with wider joints requiring exponentially more material. A 1/8-inch joint uses approximately 50% less grout than a 1/4-inch joint in identical installations.
Joint depth affects structural integrity and material consumption. Shallow joints may compromise long-term durability, whilst excessively deep joints waste material and increase costs unnecessarily.
Surface Porosity
Porous tiles absorb more grout during installation, increasing material requirements by 15-25%. Natural stone, unglazed ceramic, and textured surfaces typically demonstrate higher absorption rates.
Sealing porous surfaces before grouting reduces material waste and improves finished appearance. Pre-sealing represents a cost-effective method for controlling grout consumption on challenging surfaces.
Grout Coverage Chart by Tile Size
| Tile Size | Joint Width | Coverage per 25lb Bag | Waste Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2×2 inch | 1/16 inch | 200 sq ft | 10% |
| 4×4 inch | 1/8 inch | 120 sq ft | 12% |
| 6×6 inch | 1/8 inch | 150 sq ft | 12% |
| 8×8 inch | 1/8 inch | 180 sq ft | 12% |
| 12×12 inch | 1/8 inch | 220 sq ft | 15% |
| 18×18 inch | 1/8 inch | 280 sq ft | 15% |
| Grout Type | Typical Coverage | Application Method | Mixing Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cement-based | 25-30 sq ft/25lb | Float application | 1:4 water ratio |
| Epoxy | 35-50 sq ft/kit | Squeegee method | Pre-mixed |
| Urethane | 40-60 sq ft/tube | Direct application | Ready-to-use |
Common Mistakes in Grout Estimation
Underestimating waste factors represents the most frequent calculation error, leading to material shortages during critical installation phases. Professional installers recommend adding 15-20% waste factor for complex patterns and challenging surfaces.
Ignoring tile thickness variations causes significant calculation discrepancies, particularly with natural stone products. Hand-cut tiles may vary by 3-5mm in thickness, substantially affecting grout requirements.
Failing to account for surface porosity results in material shortages and inconsistent application. Always test grout absorption on sample tiles before finalising quantity calculations.
Grout Mixing Ratios and Consistency
Water to Powder Ratios
Proper water ratios ensure optimal grout performance and coverage efficiency. Too much water weakens the final product whilst insufficient water creates application difficulties and coverage variations.
Standard cement grout requires approximately 0.2-0.25 litres of water per kilogram of powder, depending on manufacturer specifications and environmental conditions.
Additives and Their Impact
Latex additives improve flexibility and adhesion but may alter coverage calculations by 5-10%. These additives also affect mixing ratios and working time, requiring adjusted application schedules.
Colour additives rarely impact coverage rates but may affect final appearance if mixing ratios vary between batches. Consistent mixing procedures ensure uniform colour throughout your installation.
Cost Estimation Using Grout Calculators
Accurate grout calculations enable precise budget planning by eliminating material waste and preventing emergency purchases at premium prices. Professional contractors report 10-15% cost savings through proper estimation techniques.
Consider total project costs including materials, tools, and labour when evaluating grout options. Premium grout types often justify higher initial costs through improved durability and reduced maintenance requirements.
Factor in regional price variations and supplier availability when calculating total project expenses. Bulk purchasing may offer significant savings for larger installations.
Professional Tips for Accurate Grout Calculation
Measure your installation area multiple times to ensure accuracy, particularly for irregular spaces with numerous cuts and angles. Small measurement errors compound significantly in final calculations.
Account for pattern complexity when calculating requirements. Diagonal installations, herringbone patterns, and intricate designs typically require 20-25% additional material compared to standard grid layouts.
Consider environmental factors including temperature, humidity, and ventilation when calculating working time and material needs. High temperatures may require faster application and additional material for multiple mixing cycles.
Troubleshooting Grout Calculation Issues
When calculations seem inconsistent with manufacturer specifications, verify all measurements and recalculate using alternative methods. Cross-checking ensures accuracy before material purchase.
If coverage appears insufficient during application, check for excessive waste, improper mixing ratios, or measurement errors. Document actual usage rates for future project reference.
Colour variation between grout batches often indicates calculation errors leading to mixed purchase dates. Always order sufficient material from single production runs when possible.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Factor long-term maintenance requirements when selecting grout types and calculating quantities. Premium grout options may require less frequent replacement, affecting lifecycle costs significantly.
Consider sealing requirements and maintenance schedules when evaluating total project expenses. Some grout types require annual sealing whilst others remain maintenance-free for years.
Document your grout specifications and coverage calculations for future maintenance and repair projects. This information proves invaluable for matching colours and calculating repair quantities.
Conclusion
Accurate grout calculation forms the foundation of successful tiling projects, ensuring optimal material usage whilst preventing costly delays and quality issues. Modern grout calculators simplify complex mathematics, making professional-level estimation accessible to all skill levels.
Understanding grout types, coverage factors, and calculation methods empowers informed decision-making throughout your project. Whether using manual formulas or digital tools, accurate estimation directly impacts both project success and overall satisfaction.
Investing time in proper grout calculation pays dividends through reduced costs, improved quality, and streamlined installation processes. Professional results depend on meticulous planning, and grout calculation represents a critical component of project preparation.
FAQs
Can I use the same calculator for all grout types?
Different grout types require specific calculation adjustments due to varying coverage rates and application methods. Epoxy grout calculators account for different mixing ratios and coverage characteristics compared to cement-based alternatives.
What happens if I underestimate grout requirements?
Underestimating grout quantities can halt your project and result in colour variations between batches. Emergency purchases often cost 20-30% more than planned purchases, significantly impacting project budgets.
How much extra grout should I order?
Professional installers recommend ordering 10-15% additional grout for standard installations, increasing to 20-25% for complex patterns or challenging surfaces. This buffer accounts for waste, mixing losses, and potential repairs.
